We are at the dawn of a new space age, one moving away from government funded organisations like NASA towards private companies. For example, Virgin Galactic recently became the first publicly traded human spaceflight company, while SpaceX is launching re-usable supply modules to the International Space Station.
Opportunities for suppliers are huge. But to supply the space industry, quality control must be second to none, as most spacecraft and satellites cannot be reached or returned for maintenance.
Spacecraft are rigorously tested on Earth where the stresses of launch and the severe environment of space are simulated to discover any weaknesses.
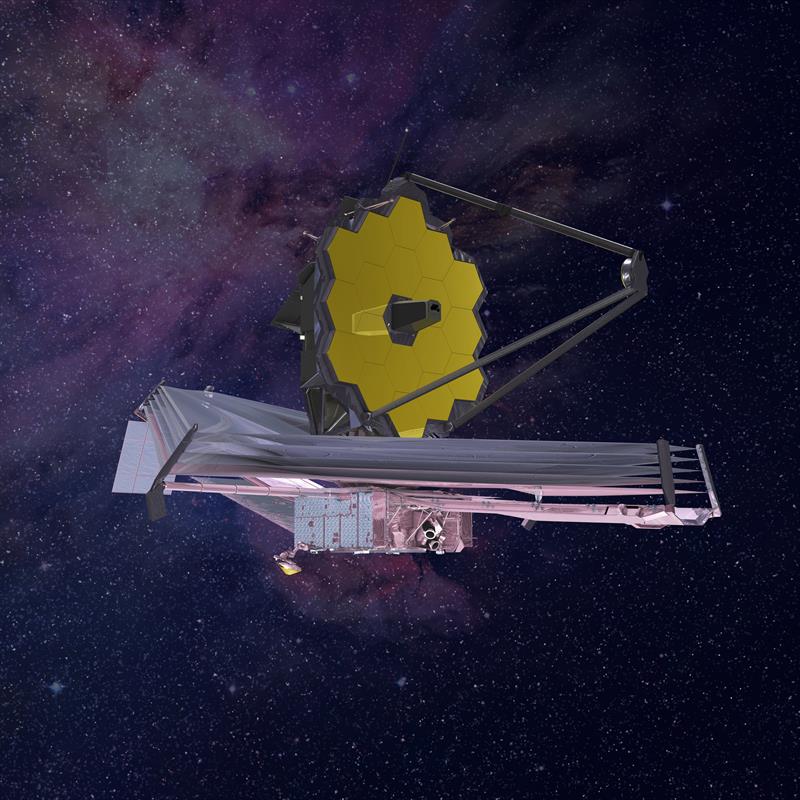
Last year, NASA delayed the launch of its James Webb Space Telescope to 30 March 2021, due to fasteners shaking loose during testing on the sun shield covers, adding $800m to the project’s original $8bn budget.
Of course, suppliers are not always in control of how their fasteners will be used and even exactly where they are going to be applied.

According to Rotherham-based Tachart (trading as Bolt and Nut Manufacturing), the key is strict adherence to specifications and recording of dimensional data with high-quality workmanship. Full material traceability is usually specified for materials originating in the European Union. Prompt delivery is required and sometimes prototypes are requested prior to bulk delivery.
Tachart says that selected materials offer strength over weight advantages and therefore production methods such as thread rolling are used. Like in Formula 1, residual swarf or loose metal clippings are of concern, therefore wire or spark eroding operations are sometimes used. Alloys usually range from strain-hardened austenitic, super austenitic, or duplex stainless steels. Age hardened titanium alloys are often specified as are some nickel alloys in certain circumstances.
Tachart’s typical fasteners for spacecraft include socket head capscrews, low head socket head capscrews, socket set screws, hex bolts, hexagon screws, bi-hex bolts, nuts, lock nuts, all-metal prevailing torque lock nuts, and plain, spring and serrated locking washers.
Typical size range is M2.5 – M12 and typical testing includes PMI, mechanical property, proof load, ultrasonic, magnetic particle MPI, dye penetrant DPI, and dimensional inspection.
Typical materials used by the company include AMS 5662/AMS 5663 (N07718), AISI 321/321S31, ISO 3506 A2-80, ISO 3506 A2-100, ISO 3506 A4-80, ISO 3506 A4-100, Ti Grade 5, Ti6Al4V, AMS4928, AlR9183, Ferralium 225, Uranus B6, Uranus 25L and Uranus S1.
More than 300 satellites were launched in 2018, bringing the total number of satellites in orbit to 2100. Many are small satellites that will widen communication networks for a host of applications, enabling 24 million IoT connections by 2024, according to ABI Research. This is a lucrative market that will only continue to grow over time.