Specialist UK fixing systems producer, Adhesion Technologies Ltd (ATL) is launching its latest fastening solution, Fiba Spida, primarily designed and engineered for FRP composites. This new fastening system is claimed to give designers and manufacturers of glass and carbon fibre FRP moulded parts more design freedom than alternative fixing systems. The added benefit of saving production time boosts output rates and productivity.
Fiba Spida is an all-in-one fastener and ‘tow steered’ reinforcement fabric fixing system, based on ATL’s Spida fixings and proprietary adhesion enhancing technologies. The most popular Spida fastening is the M bolt type threaded stud and nut system, but Spida is a Universal Fixing System that can support studs, nuts, spacers, conduit strapping, spikes, cable trees, cable, and embedded electrical circuits.
The design and technologies used in Spida and Fiba Spida fixings enables applied stresses to be spread across a larger part of the substrate, so smaller and fewer fixings can be specified in some applications, reducing the overall weight of an assembled component.
For composites part producers in particular, the Fiba Spida fixings – with glass and carbon fibre options – are said to offer significant design, productivity, production, cost reducing and performance enhancing benefits. These benefits have attracted growing interest in the last three years from buyers and design engineers in the rail, mining, automotive, marine, medical equipment and industrial market sectors.
‘Hybrid’ fixing system
This product development combines ATL’s Spida stud and parabolic base fixing system and patented AdMax base surface area enhancing treatment, which provides a stronger resin bond, with the new ‘tow steered’ technology – the ‘Fiba’ part of this new fixing system. The innovative tow steering production system avoids cutting the glass or carbon fibres by guiding the fibre tows around either a metal or engineering plastic threaded Spida bolt/stud, so maintaining the maximum possible reinforcement strength from the fibres.
The next production step is to high pressure inject a compatible resin which encapsulates the Spida bolt/stud, base and ‘locks in’ the glass or carbon fibre fabric option to produce the final Fiba Spida fixing; depending on the application, either a single or double fabric layer for interleaving can be produced.The overall result is a high performance ‘hybrid’ fixing system with a built-in quadraxial fabric reinforcement system, which can handle higher tensile and torsional loads as point loads and cluster stresses in the fabricated component are dissipated over a much wider area.
Versatile fixing
Fiba Spida fixings are supplied fully assembled and are suitable to apply fixings in a new build component or to upgrade fixing requirements as part of a maintenance, repair or refurbishment project.Fiba Spida has been designed so that a fixing can be quickly and accurately positioned in a mould during the dry layup pre-moulding stage, with no additional preparation needed. Alternatively, it can be bonded or overlaminated to the surface of an existing moulded part that needs fixings.
Fiba Spida has solved several challenging fixing applications, such as how to apply a fixing onto a thin, honeycomb sandwich laminate under 200g, where using a traditional drilled screw, helicoil, potted insert or bonded base/stud fixing would not work in practice, as typically the top skin is pulled off under load. Unlike other fixings, due to its load spreading design, when a load is applied to Fiba Spida fixings the surface skin of the honeycomb sandwich laminate does not pull off.
For use with other structural materials, such as wood and metal, Fiba Spida fixings can be secured onto the outer surface where needed by overmoulding using a compatible thermoset resin for the glass or carbon fibre fabric and the substrate. For building and construction applications, Fiba Spida fixings can be dry positioned and permanently set into or onto concrete.
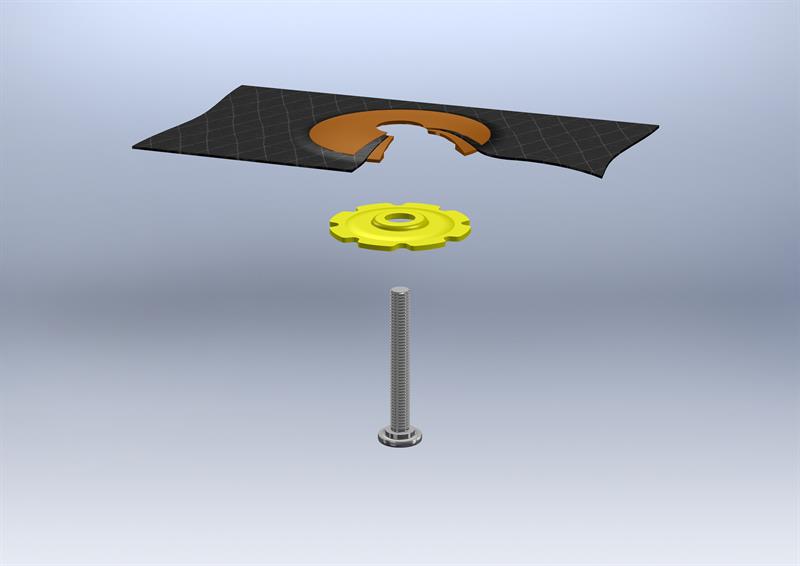
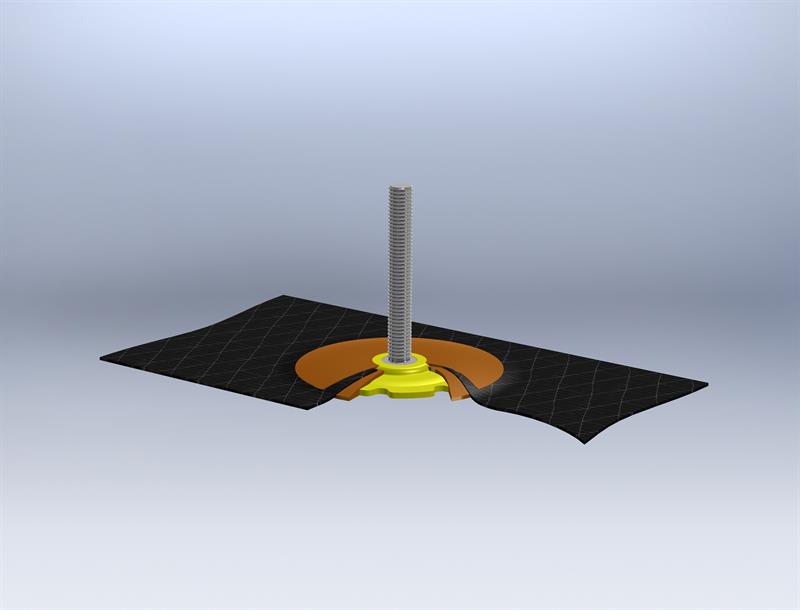
Tow steered benefits
ATL’s automated tow steering production method avoids damaging the glass or carbon fibres by moving fibre bundles apart to create the fastening stud hole rather than drilling or cutting; according to ATL, drilling a 5mm rivet hole severs 96,000 stress dissipating filaments per 1000 grams of fabric. The integrity of the original long fibres is maintained, avoiding weak spots and any loss of reinforcement performance, enabling a Fiba Spida fixing to cope with higher stress loads.
The tow steering method of producing Fiba Spida fixings enables ATL to offer designers and manufacturers a higher performing, alternative mechanical fixing solution, which not only increases productivity, but can also reduce weight and material costs. This is because, for many designs, fewer fastening points, smaller studs and bases and less fabric are needed compared to using hole punched, cut or drilled reinforcement fabrics in combination with a conventional welded stud and base fastening of equivalent specification.
Fastening material options
The Fiba Spida product range offers design engineers a choice of high-performance specification metal and plastic fastener materials, along with a quadraxial stitched fabric (from 600 grams) in either carbon or E-glass fibres to suit resin types and application needs. All Spida studs, threaded standoffs and bases can be used separately or as a complete fixing.The current Fiba Spida standard range is available in M4, M6, M8, M10 and M12 threaded stud/nut diameters in combination with a standard 53mm diameter (1.8mm thick) base, available in three standard cold formed metal options: brass; passivated 316L stainless steel (austenitic marine grade); zinc-nickel plated, heat treated (20MnB4/CR4 rated) carbon steel. Standard stud lengths range from 20mm to 60mm.
ATL operates a highly flexible production service able to cope with manufacturing bespoke fixings. Order quantities are dependent upon the design and material specification required, with limited volume orders accepted to support new product development projects.
Proven technology
More than five years of R&D has been carried out to establish that autogenously welding the stud to the base maximised the ultimate breaking load performance of this critical joint.
The proprietary design and adhesion technology used for Spida fixings creates a much higher strength bond with a wide range of substrates. This includes the optional proprietary AdMax surface treatment which is standard on Fiba Spida fixings; having the AdMax coating increases the bond surface area, adhesion surface energy and wicking properties, improving the bond strength. The overall adhesion performance can be up to 56% greater than alternative solutions. The Admax coating also increases metal strength and density, ensuring a stronger fixing.
Spida bases also have several key design features to further improve adhesive performance. These include castellated anti-torsion edges which enable the adhesive to form lugs; these castellated edges provide 24% greater torsional resistance strength than circular fixings. The concave shaped inner section of the base design creates a ‘micro chamber’ in which the long chain molecules of the adhesive can orientate from zero to 180 degrees during curing, resulting in enhanced peel, shear, torsion, cleavage, tension and compressive loading capabilities.
The overall result is a significantly stronger method of mechanically joining metal, composite and other engineering materials together with enhanced peel, shear, torsion, cleavage, tension and compressive loading capabilities. This is supported by validated data, following a long-term performance testing programme carried out by approved global fastening component suppliers: Barton Cold Form, Australian Parts & Equipment and at the Research Institute for Industry (RIfI) at the University of Southampton.
Ongoing trials
Testing and market trials to reduce manufacturing costs and make weight savings are currently underway with several existing and potential customers;these trials are being carried out in rail infrastructure, military equipment, medical equipment, leisure and working boats, drones and helicopter interiors. Production trials are also being carried out to evaluate possible productivity gains achievable with both Spida and Fiba Spida fixings.
Examples of ongoing trials include a major producer of medium sized drones, which is currently evaluating Spida fixings, as well as using AdMax base coating system for upgrading the adhesion performance of various metallic components bonded to composite substrates. Interior aircraft FRP applications are being evaluated by another customer, which is looking to redesign using Fiba Spida fixings in pilot and passenger seating, shelving, partitioning, panelling and avionics boxes.
NATEP aviation project testing
As part of an ongoing NATEP (The National Aerospace Technology Exploitation Programme) consortium project, extended accreditation testing, and application trials are also being carried out on ATL’s Fiba Spida fixing system by a leading helicopter OEM looking to reduce weight and significantly reduce production times and costs.
Independent comparative bearing cross testing is ongoing to assess the performance of Fiba Spida’s tow spreading technology against existing aviation approved highlight pins and rivets. Results and findings from the laboratory tests will be published in the next few months, once all the comparative testing for tensile, shear and torsion performance have been completed for a variety of metallic and non-metallic fastening materials.
In-house testing
In-house destructive testing using a specially designed fixture strength test rig is carried out by ATL, which has proven from extensive comparative test data that bonded fasteners don’t behave like traditional fixings, nor do they conform to traditional DIN or ISO standards and failure modes.
Testing a hybrid fixing, such as Fiba Spida, is even more complex. Performance varies depending on whether the fixing has been included within the substrate during production or added as a secondary stage onto the surface. Different types of substrate materials and part thickness affects both the fixing performance and the type of failure.With a Fiba Spida fixing, its positioning within a substrate, the choice of glass or carbon fibres, the size of the fabric piece used and if it is single or double layered, all make a significant difference to its fixture performance in use.
Based on their findings, ATL recommends a customised approach depending on the maximum fixing performance strength and failure mode required for an application. For example, a Fiba Spida fixing with a mild steel M8 bolt fixing combined with a 3600g E-glass fabric fails due to breakage of the bolt head; the same M8 bolt used with a 1200g carbon fibre fabric specified for the Fiba Spida fixing results in failure due to the substrate panel breaking.




